Stress is a common experience that can significantly impact mental health and overall well-being. Employing effective stress management techniques can help reduce the stress response and mitigate the effects of chronic stress. By incorporating strategies such as mindfulness, regular exercise, and proper time management, individuals can build resilience against daily stressors.
Many people overlook the importance of addressing stress in their lives. The consequences of untreated stress often lead to more severe health issues, both mentally and physically. Learning how to manage stress not only promotes better mental health but also enhances the ability to cope with life’s challenges.
In this exploration of stress management techniques, practical methods and actionable insights will be provided. Readers can expect to find approaches that fit various lifestyles, enabling them to take control of their stress and improve their quality of life.
Understanding Stress and Its Impact on Health
Stress can significantly influence both mental and physical health. It triggers complex biological responses that affect various body systems and can lead to chronic health issues if not managed effectively.
The Science of Stress Response
When faced with a stressor, the body activates the fight-or-flight response. This response triggers the release of hormones like adrenaline and cortisol.
- Adrenaline: increases heart rate and energy supplies.
- Cortisol: helps regulate metabolism and immune response.
These hormones prepare the body to respond to perceived threats. While this response is beneficial in short bursts, prolonged activation can lead to health problems.
Physical and Psychological Effects of Stress
Stress affects both the body and mind. Physically, it can lead to elevated blood pressure, tension headaches, and fatigue. One common outcome is insomnia.
Psychologically, stress can affect mood and lead to conditions such as depression and increased irritability.
Managing stress is crucial for maintaining physical health and well-being.
Chronic Stress and Health Risks
Chronic stress poses significant health risks. Prolonged exposure to stress hormones can weaken the immune system, making an individual more susceptible to infections.
Moreover, it increases the risk of heart disease and hypertension.
Unmanaged stress can also lead to other serious issues, including mental health disorders. Recognizing the signs of stress early can aid in effective management.
Core Stress Management Techniques
Effective stress management techniques can greatly improve emotional well-being. These methods help individuals better cope with stressors in daily life. Key practices include cognitive behavioral therapy, mindfulness, physical exercise, and various relaxation techniques.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy is a structured approach that focuses on identifying negative thought patterns and behaviors contributing to stress. It encourages individuals to challenge and reframe these thoughts. By replacing irrational beliefs with more rational, realistic ones, clients experience reduced anxiety and improved coping skills.
CBT sessions often involve self-monitoring and strategies to manage stress in real time. Worksheets and exercises may help individuals track their thoughts and behaviors, promoting awareness and change. This technique is widely used and backed by research, showing its effectiveness in managing conditions like anxiety and depression.
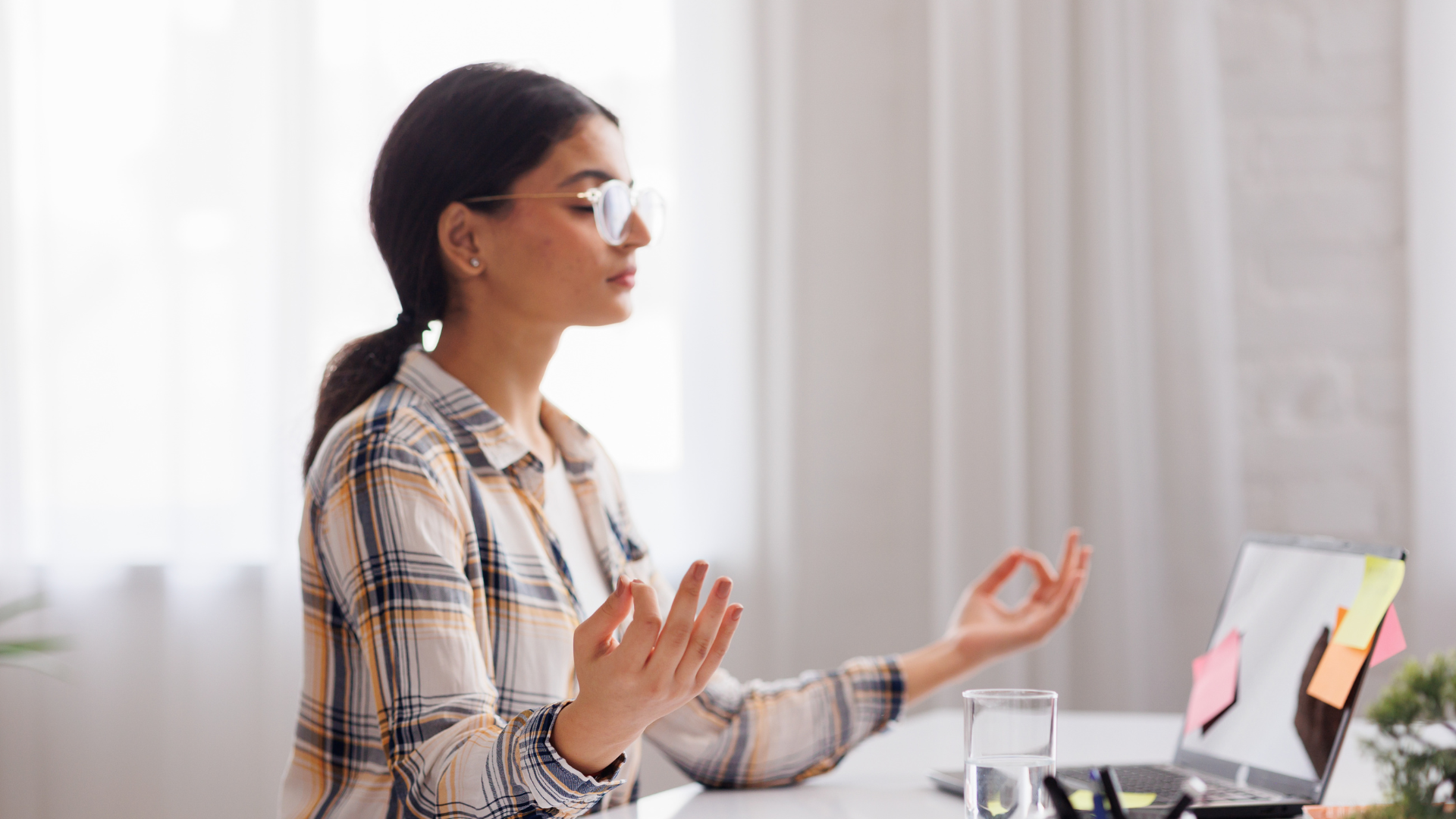
Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness and meditation practices help individuals stay present in the moment, reducing feelings of overwhelm. Mindfulness includes techniques like deep breathing and body scanning, promoting relaxation and mental clarity. Meditation can involve guided sessions or self-directed practices that encourage a focus on one’s breath or a specific mantra.
Research indicates that regular mindfulness practice can decrease cortisol levels, the hormone associated with stress. Individuals often report improved focus and emotional regulation after integrating these practices into their daily routines. Classes or apps can provide helpful resources to begin practicing mindfulness and meditation.
Physical Exercise and Activity
Physical exercise is a powerful tool for stress management. Engaging in regular physical activity releases endorphins, chemicals in the brain that act as natural painkillers and mood elevators. Activities like walking, running, or yoga can help reduce muscle tension and promote relaxation.
It is recommended to aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Finding enjoyable activities increases adherence to exercise routines. Group classes or outdoor activities can provide additional motivation and social support, enhancing the overall stress-relief experience.
Relaxation Techniques and Deep Breathing
Relaxation techniques, including deep breathing exercises, promote calmness and reduce stress levels. Deep breathing involves taking slow, controlled breaths to lower heart rate and blood pressure. Techniques like progressive muscle relaxation systematically tense and relax muscle groups, alleviating physical tension.
Incorporating these techniques into daily life can lead to improved emotional resilience. Short, regular practice sessions, even just five minutes a day, can yield significant benefits. Various guided recordings and apps are available to assist individuals in mastering relaxation techniques, making them accessible anytime, anywhere.
For a better experience with these techniques, it might be helpful to do them in a setting where the air quality is good. Some individuals may prefer to do them outdoors; others prefer the comfort of indoors. For those who do breathing exercises indoors, it can be beneficial to ensure the indoor air quality is healthy. Various factors, like mold growth or lack of ventilation, can affect this. In order to prevent such problems, homeowners can consult professionals who provide services like heat ducting and Mold Testing in Clive, IA (or elsewhere).
Building a Resilient Lifestyle
A resilient lifestyle encompasses healthy habits, strong social connections, and a well-managed work-life balance. Each of these components contributes to an individual’s ability to cope with stress and maintain overall well-being.
Developing Healthy Habits
Adopting healthy habits is crucial for building resilience. This includes maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Proper nutrition fuels the body and mind, helping to regulate mood and stress levels.
Regular physical activity also plays a vital role. Engaging in exercise releases endorphins, which can improve mood and promote a sense of well-being. Pairing fitness with adequate sleep routines enhances recovery and cognitive function. Aiming for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night is essential.
Practicing gratitude can further strengthen mental resilience. Taking the time to reflect on positive experiences fosters an optimistic outlook, reducing stress and improving emotional stability. Such habits create a strong foundation for effectively managing life’s challenges.
Foster Strong Relationships and Social Support
Strong relationships provide significant stress relief. Individuals are encouraged to cultivate connections with family and friends, fostering a support network that can be invaluable during tough times. Sharing experiences and emotions can alleviate feelings of isolation.
Participating in social activities or community groups can enhance these connections. Leisure activities offer opportunities to bond with others over shared interests, promoting a sense of belonging. These interactions contribute to emotional stability and personal growth.
Supporting others within this network also builds resilience. Offering help creates a reciprocal relationship where both parties benefit from mutual support. Prioritizing these connections equips individuals with resources to navigate stress more effectively.
Maintaining Work-Life Balance
Achieving a healthy work-life balance is essential for resilience. Individuals should set clear boundaries between work and personal time, ensuring that neither encroaches on the other. This separation helps prevent burnout and promotes mental clarity.
Scheduling regular leisure activities can enhance this balance. Engaging in hobbies or spending time with loved ones allows for relaxation and rejuvenation. It’s important for individuals to reserve time for self-care and personal interests.
Employers can also foster a healthy work environment by promoting flexible schedules and mutual respect for personal time. This cooperation creates a culture that values well-being, further reinforcing the resilience of the workforce.
Strategies for Coping with Acute Stressors
Acute stressors can arise unexpectedly, creating immediate pressure. Effective approaches to coping involve recognizing stress triggers, implementing problem-solving techniques, and regulating emotions through acceptance.
Identifying and Managing Stress Triggers
Recognizing stress triggers is the first step in effective stress management. Triggers can be external, such as deadlines or conflicts, or internal, like self-doubt. Keeping a stress diary helps individuals pinpoint patterns and recognize recurring situations that generate stress.
Once triggers are identified, strategies to manage them can be employed. This may involve setting realistic deadlines, improving communication skills, or developing assertiveness. The key is to take action by addressing the sources of stress directly or adjusting one’s response to them.
Effective Problem-Solving Techniques
Problem-focused coping is essential for managing acute stressors. This approach involves breaking down overwhelming tasks into smaller, manageable steps. Creating a prioritized list can help individuals focus on what needs to be accomplished first.
Additionally, brainstorming solutions empower individuals to take charge. This may include seeking advice from trusted colleagues or friends. Adopting a mindset of optimism can also foster resilience, allowing individuals to view challenges as opportunities for growth rather than insurmountable obstacles.
Emotion Regulation and Acceptance
Emotion-focused coping strategies help individuals manage their emotional responses to stress. Techniques such as mindfulness and deep breathing exercises can enhance emotional regulation. Practicing awareness of one’s feelings allows for a more balanced response to stressors.
Acceptance plays a crucial role in coping with stress. Rather than resisting uncomfortable emotions, embracing them helps to reduce their intensity. Commitment to self-care practices, such as regular exercise and healthy eating, supports emotional well-being and builds resilience in the face of acute stress.